|
MotifSuite provides a platform for de novo regulatory motif detection using a stochastic motif detection algorithm with various motif assessment tools. The suite revolves around MotifSampler, a de novo motif detection tool based on Gibbs sampling that searches for an overrepresented motif in a set of coregulated input sequences. In addition to the core sampler, MotifSuite provides tools to automatically merge the results of multiple stochastic sampling runs and to perform downstream analyses.
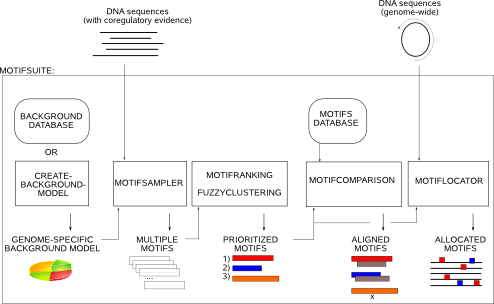
When used as an integrated flow, MotifSuite guides you through the whole process of de novo motif detection going from the selection of a background model, the actual Gibbs sampling, summarizing the output of multiple Gibbs sampling runs, till screening the remainder of the genome with the retrieved motif models (Fig.1, read more in MotifSuite overview). Alternatively, each application within MotifSuite can be used separately and has its own entry page. Submission will initiate the software command on our server where you can download the applications'output files from.
Optionally, a stand-alone executable of each application can be downloaded for use on your own platform.
The suite consists of the following functionalities:
- generation of a genome-specific background model which can be selected from our database or compiled using CreateBackgroundModel.
- generation of a conservation-based Position Specific Prior (PSP): CreateConservationPSP allows to bias the motif search to a priori prioritized well-conserved DNA regions in a sequence.
- de novo motif detection by means of MotifSampler. MotifSampler is a Gibbs sampling based de novo motif detection algorithm that performs multiple searches for candidate regulatory motifs. Its output is a long list of redundant and not necessarily all relevant solutions.
- prioritizing motifs: we provide tools to postprocess the output of multiple runs of a Gibbs sampling algorithm (or any other stochastic motif detection algorithm). MotifRanking reorganizes the multiple motif detection solutions (PWMs) in a shorter list of non-redundant motifs sorted by their motif score. FuzzyClustering constructs consensus motifs by analyzing the multiple motif detection solutions at their instance level.
- comparing motifs: MotifComparison analyzes if your detected motif (PWM) corresponds to any of previously described motif models reported in curated databases or detected by yourself in previous analyses.
- genome-wide screening: MotifLocator scans a given set of genome-wide sequences for potential novel instances of your detected motif.
|


 To: Our group ; Contact us ; citing MotifSuite
To: Our group ; Contact us ; citing MotifSuite