To: Guidelines

To: Guidelines

This page is linked to MotifSampler Guidelines and should be read accordingly. |
Extra : construction of W(s|Sk) and Pr(x|Sk). |
|
(back to : guidelines) 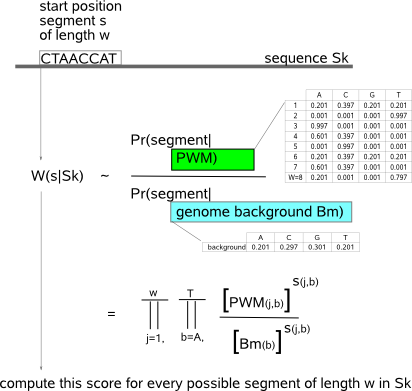 The nominator of the segment score is computed by multiplying the probabilities for each position in the segment to be a motif. These probabilities are the PWM frequencies computed in the preceding update step. In the same way, the denominator multiplies the probabilities for each position in the segment to be non-functional background. Background probabilities are the (user-supplied) frequencies in the transition matrix of the background model (parameter -b). If a segment is assigned as being a motif instance in the last iteration step, the segment score of this instance is reported in the text output file -o. 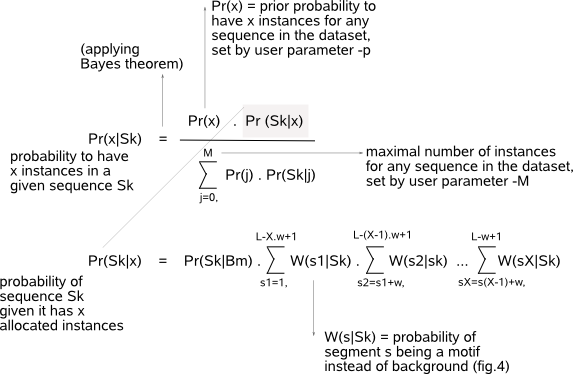 The computation of Pr(x|Sk), the probability to have x instances of a motif in a given sequence Sk, is based on two factors (fig.5a) : 1) Pr(x), the prior probability to have x instances in a sequence which is described in parameter -p and 2) Pr(Sk|x), the -internally computed- probability of sequence Sk given there are x instances of a motif allocated in this sequence. As shown in the formula for Pr(Sk|x) in fig.5a and illustrated in the example Pr(Sk|2) in fig.5b, the term Pr(Sk|x) is computed based on the segment scores W(s|Sk) of all possible instances in this sequence. In words, for a given value x, the formula for Pr(Sk|x) sums the likelihood of every possible combination of x instances in the sequence, where the likelihood of one particular combination of x instances is computed as the product of the individual segment scores of each of the x instances. This means that when multiple instances have high segment scores (which is the case when they all represent the same true motif), the contribution of the second term Pr(Sk|x) to the probability distribution Pr(x|Sk) to allocate multiple instances in sequence Sk will also be high. The denominator in the formula for Pr(x|Sk) is a normalizing factor to convert the computed likelihoods into a probability distribution. We offer a wide range of prior probability distributions for the user to choose from as described in -p Priors. |
Feedback |
|
Contact us if you have comments, questions or suggestions or simply want to react on the contents of this guideline. Thank you. |